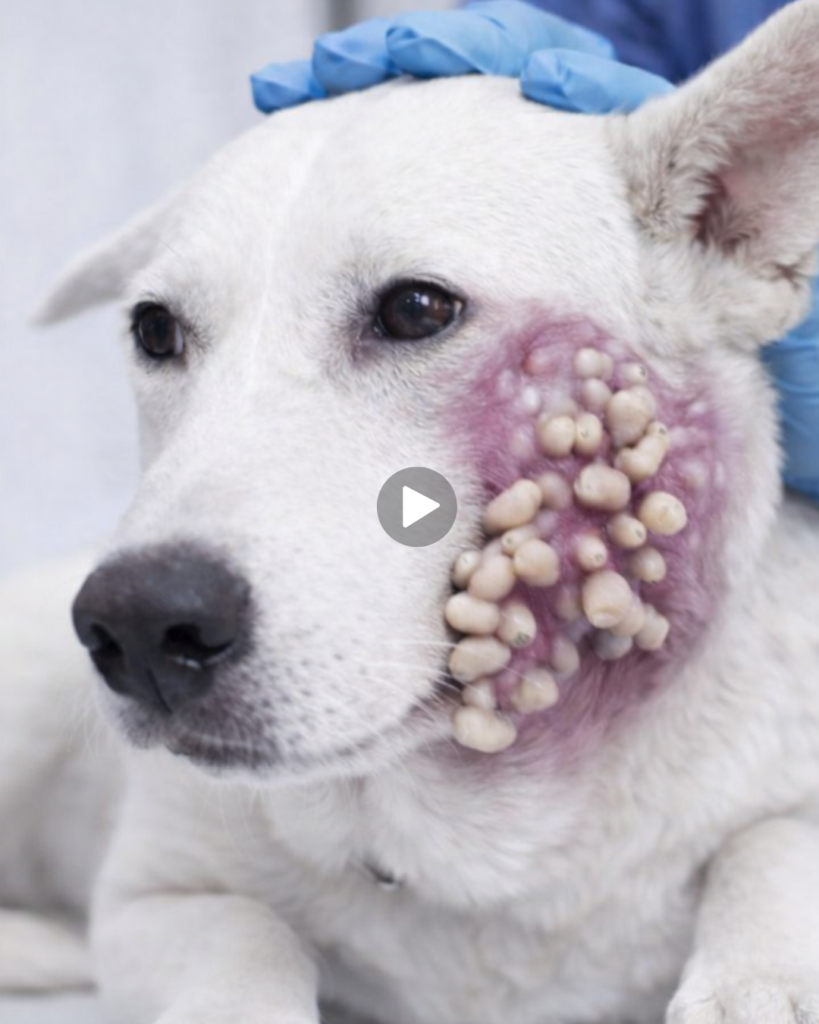
Skin diseases are among the most common health problems affecting dogs, and facial skin conditions can be especially alarming for pet owners. The image above shows a dog undergoing veterinary examination with a severe facial skin lesion characterized by clustered nodules, swelling, and inflammation on the cheek. Such conditions not only affect a dog’s appearance but can also cause pain, discomfort, and serious health complications if left untreated. Understanding the possible causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for every responsible pet owner.
Common Causes of Facial Skin Lesions in Dogs
Facial growths and lesions in dogs can occur due to several reasons. One of the most common causes is parasitic infestation, such as fly larvae (commonly known as mango worms or cutaneous myiasis). These parasites lay eggs on the dog’s skin, which hatch and burrow into the tissue, forming painful nodules.
Another possible cause is bacterial or fungal infections. Deep skin infections, also called pyoderma, can lead to abscesses, pus-filled nodules, redness, and swelling. Fungal infections may develop in humid environments or in dogs with weakened immune systems.
Tumors and cysts are also a concern. Benign growths like sebaceous cysts or papillomas may appear as lumps, while malignant tumors can cause aggressive tissue damage. Only a veterinary biopsy can confirm whether a growth is cancerous or non-cancerous.
Additionally, allergic reactions, insect bites, or untreated wounds can worsen over time, leading to secondary infections and severe inflammation, especially on sensitive areas like the face.
Visible Symptoms and Warning Signs
Dogs suffering from serious facial skin conditions often show visible and behavioral symptoms. These may include:
- Swollen or hardened areas on the face
- Clusters of nodules or wart-like growths
- Red, purple, or inflamed skin
- Discharge, pus, or bleeding from lesions
- Hair loss around the affected area
- Excessive scratching, rubbing, or pawing at the face
- Lethargy, reduced appetite, or signs of pain
In advanced cases, dogs may become aggressive or withdrawn due to discomfort. Facial lesions can also interfere with eating, breathing, or vision if swelling spreads.
Importance of Early Veterinary Diagnosis
Prompt veterinary attention is crucial when any abnormal growth or swelling appears on a dog’s face. As shown in the image, a trained professional uses gloves and medical tools to safely examine the affected area. Veterinarians may perform diagnostic tests such as skin scrapings, biopsies, blood tests, or imaging to determine the exact cause.
Early diagnosis allows for targeted treatment, reduces suffering, and significantly improves recovery outcomes. Delaying treatment can lead to infection spreading deeper into tissues or even into the bloodstream.
Treatment Options for Facial Skin Conditions
Treatment depends entirely on the underlying cause. For parasitic infections, the veterinarian may remove larvae manually and prescribe antiparasitic medications. Antibiotics are commonly used to treat bacterial infections, while antifungal drugs address fungal causes.
In cases of abscesses or severe swelling, surgical drainage may be required. Pain relief medications and anti-inflammatory drugs help manage discomfort during recovery. If tumors are diagnosed, surgical removal, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy may be recommended depending on severity.
Topical treatments such as medicated creams, antiseptic washes, or sprays are often used alongside systemic medications. Owners must follow the veterinarian’s instructions strictly and complete the full course of treatment to prevent recurrence.
Prevention and Home Care Tips
Preventing facial skin conditions starts with good hygiene and regular health checks. Pet owners should:
- Inspect their dog’s skin weekly for unusual lumps or redness
- Keep dogs clean and dry, especially in warm climates
- Use parasite prevention treatments regularly
- Avoid leaving wounds untreated
- Maintain a balanced diet to support immune health
- Schedule routine veterinary checkups
For outdoor or stray dogs, extra care is required, as they are more vulnerable to parasites and infections.
Conclusion
Facial skin conditions in dogs can range from mild to life-threatening, and the visual impact can be distressing for both pets and their owners. The condition shown in the image highlights the importance of early detection, professional veterinary care, and proper treatment. With timely intervention and responsible pet ownership, most dogs can recover fully and return to a healthy, comfortable life.
Educating yourself about the signs and causes of canine skin diseases is the first step toward protecting your pet’s well-being and ensuring they receive the care they deserve.