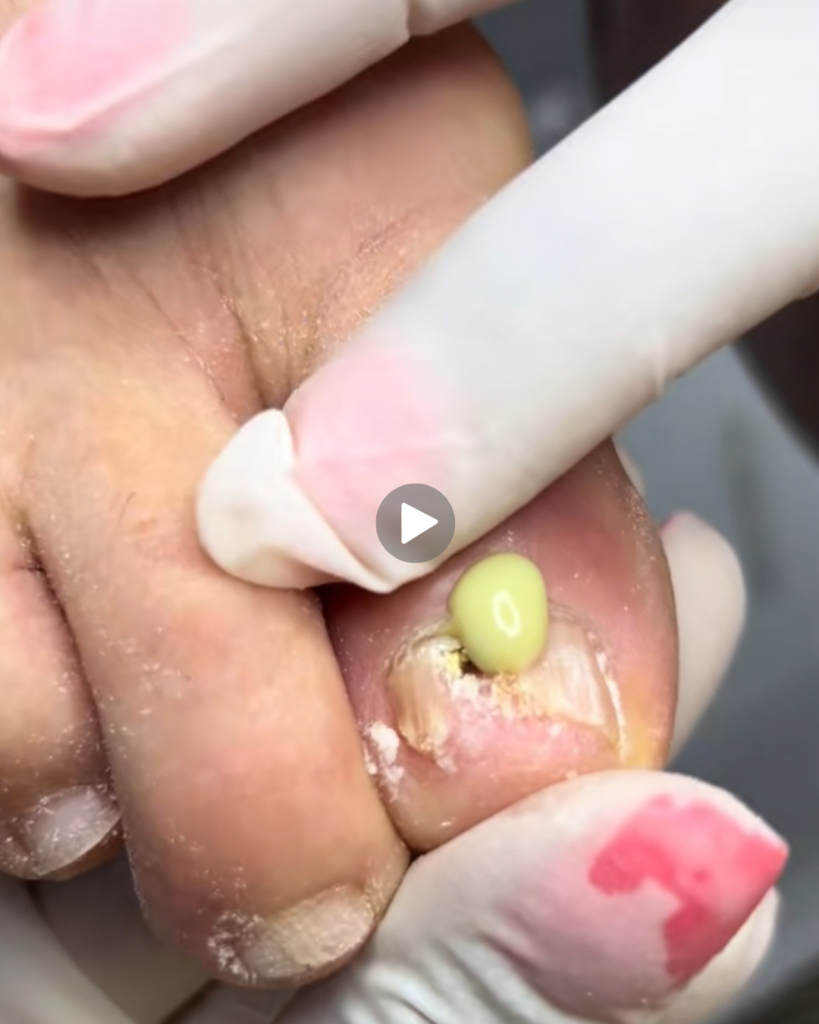
A toenail abscess is a painful condition that occurs when bacteria infect the tissue around or under the toenail, leading to a buildup of pus. It is often caused by an ingrown toenail, minor injuries, tight footwear, or poor foot hygiene. While mild cases can sometimes be managed at home, toenail abscesses should never be ignored because untreated infections can worsen and spread. Knowing how to care for a toenail abscess at home—and when to seek medical help—is essential for protecting your foot health.
What Is a Toenail Abscess?
A toenail abscess is a localized infection characterized by swelling, redness, warmth, pain, and pus formation near the nail. The big toe is most commonly affected. Bacteria enter through small cuts, cracks, or areas where the nail pierces the surrounding skin. People with diabetes, poor circulation, or weakened immune systems are at higher risk of complications and should be especially cautious.
Signs and Symptoms
Common symptoms of a toenail abscess include:
- Throbbing or sharp pain
- Swelling around the nail
- Redness and warmth
- Yellow or white pus
- Difficulty walking or wearing shoes
- In some cases, fever or spreading redness
If the pain is severe or symptoms worsen, home treatment may not be sufficient.
Can a Toenail Abscess Be Treated at Home?
Very mild abscesses in otherwise healthy individuals may respond to early home care. However, if there is a large amount of pus, intense pain, fever, or spreading infection, professional medical treatment is necessary. Never attempt to cut deeply into the skin or drain an abscess aggressively at home, as this can cause serious infection.
Safe Home Treatment Steps
1. Warm Saltwater Soaks
Soak the affected foot in warm water mixed with salt for 15–20 minutes, 2–3 times a day. This helps reduce swelling, improves blood flow, and may encourage natural drainage. Epsom salt can also be used if available.
2. Keep the Area Clean and Dry
After soaking, gently dry the foot with a clean towel. Keeping the area clean prevents bacteria from spreading. Avoid walking barefoot in public areas while the infection is present.
3. Apply an Antiseptic
Use an over-the-counter antiseptic solution or ointment to reduce bacterial growth. Apply it gently around the nail, not deep into the skin.
4. Use a Clean Bandage
Cover the toe with a sterile bandage to protect it from friction and contamination. Change the bandage daily or whenever it becomes wet or dirty.
5. Elevate the Foot
Elevating your foot when resting can help reduce swelling and throbbing pain.
6. Wear Proper Footwear
Avoid tight shoes or socks that put pressure on the affected toe. Choose open-toed or loose-fitting footwear until healing begins.
Pain Management
Mild pain can usually be managed with over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, unless you have a medical condition that prevents their use. Do not apply numbing creams unless recommended by a healthcare professional.
What NOT to Do at Home
- Do not squeeze or pop the abscess
- Do not cut the nail or skin deeply
- Do not use sharp or unsterilized tools
- Do not ignore worsening symptoms
Attempting to drain an abscess yourself can push bacteria deeper into the tissue, increasing the risk of serious infection.
When to Seek Medical Attention
You should see a doctor or podiatrist immediately if:
- The abscess does not improve after 2–3 days of home care
- Pain becomes severe or unbearable
- Redness spreads beyond the toe
- You develop a fever
- You have diabetes, nerve damage, or poor circulation
- There is a foul smell or excessive pus
Medical treatment may include professional drainage, antibiotics, or partial nail removal in cases caused by ingrown toenails.
Preventing Future Toenail Abscesses
Prevention is key to avoiding recurring infections.
- Trim toenails straight across, not rounded
- Avoid cutting nails too short
- Wear properly fitted shoes
- Keep feet clean and dry
- Treat ingrown toenails early
- Avoid nail injuries and trauma
Regular foot care is especially important for athletes and people who spend long hours on their feet.
Conclusion
A toenail abscess can be painful and disruptive, but early and gentle home care may help mild cases heal. Warm soaks, cleanliness, protection, and proper footwear can reduce discomfort and support recovery. However, toenail abscesses can become serious if mishandled. If symptoms worsen or fail to improve, seeking medical care is essential. Treating the problem promptly and safely will protect your toe, prevent complications, and restore comfort more quickly.
